Routine postoperative imaging may improve pancreatic cancer survival
Research suggests that patients who are invited for routine imaging after pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma resection have significantly longer overall survival than those who undergo imaging only after the development of symptoms.
Impact of haematological malignancy on pregnancy revealed

Women who are diagnosed with haematological malignancies during pregnancy have similar overall survival to peers diagnosed within a year of their pregnancy ending, indicates research published in The Lancet Haematology.
European retinoblastoma report shows stabilised incidence, high 5-year survival

The incidence of retinoblastoma in children in Europe stabilised between 2000 and 2013, say EUROCARE-6 Working Group investigators who report high 5-year survival rates in this population.
Fear of recurrence persists for decades among paediatric cancer survivors
A third of adults who survive childhood cancer continue to have a fear of cancer recurrence for decades after their diagnosis, highlights research published in JAMA Network Open.
First-line trabectedin use boosts OS for advanced leiomyosarcoma
LMS-04 trial findings show a significant overall survival benefit with the use of induction and maintenance trabectedin alongside first-line doxorubicin for patients with inoperable, advanced leiomyosarcoma.
Annual screening supported for people at high-risk of pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma

Findings from the Cancer of the Pancreas Screening program in the USA support the use of annual endoscopic ultrasound or magnetic resonance imaging for patients with a familial or genetic predisposition for pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma.
Surveillance effective for childhood cancer predisposition syndrome management
Early detection of tumours in children with a cancer predisposition syndrome can be achieved with standardised surveillance protocols, US cohort study findings demonstrate.
Phoenix Sepsis Score ‘accurate’ for children undergoing cancer treatment
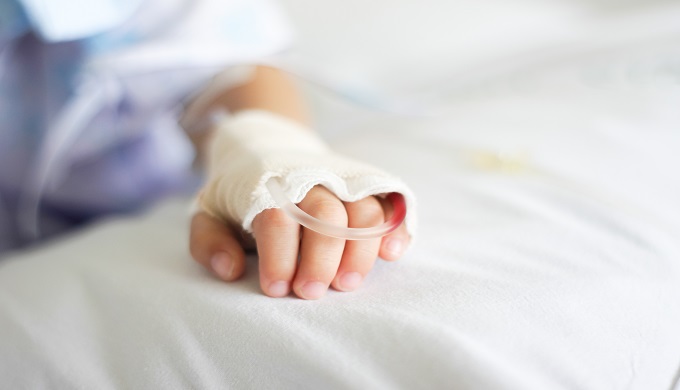
The Phoenix Sepsis Score “accurately” characterises the risk of definitely attributable mortality from sepsis and the duration of intensive care unit stay in children undergoing cancer treatment who have a suspected infection, US researchers report.
Pharmacogenomic-guided induction therapy might reduce pediatric AML racial disparities

Using a pharmacogenomic strategy to guide choice of induction therapy for acute myeloid leukaemia might help overcome the disparity in outcomes between Black and White children, suggests research published in JAMA Network Open.
Increasing measurable residual disease level predicts poorer AML outcomes

Research demonstrates a dose-dependent correlation between measurable residual disease and the likelihood of relapse and poor overall survival among adults with acute myeloid leukaemia who achieve complete remission before undergoing allogeneic haematopoietic cell transplantation.