Minimally invasive surgery improves antihypertensive management in MACS
Surgery to remove all or part of an adrenal gland can help reduce hypertension in people with unilateral incidentalomas and mild autonomous cortisol secretion, suggest findings from the CHIRACIC study.
Elinzanetant reduces vasomotor symptoms during breast cancer endocrine therapy

The neurokinin-targeted agent elinzanetant significantly improves vasomotor symptoms in women undergoing endocrine therapy for hormone receptor-positive breast cancer, research indicates.
Psychiatric medication use linked to increased ALS risk and worsening survival

Treatment with common psychiatric medications may be associated with an increased risk of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis, suggests a case-control study published in JAMA Network Open.
Solid tumour CAR T-cell therapy achieves PFS gain in gastric cancer
The first randomised controlled trial of a CAR T-cell therapy in solid tumours has achieved a significant improvement in progression-free survival for patients with advanced gastric or gastro-oesophageal junction cancer compared with physician’s choice of therapy.
Mastectomy, salpingo-oophorectomy improve BRCA breast cancer patient survival
Risk-reducing surgery leads to improved overall survival for breast cancer patients carrying a BRCA1 or BRCA2 mutation, confirm two studies published in The Lancet Oncology.
Support for amiloride as a spironolactone alternative in resistant hypertension
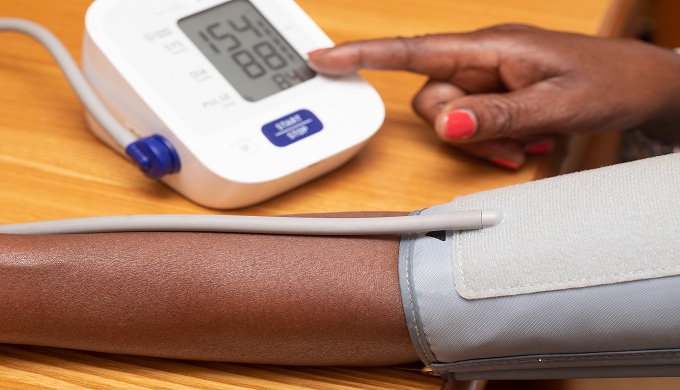
The diuretic amiloride may be a suitable treatment alternative to spironolactone for patients with resistant hypertension, suggests a study published in JAMA.
Childhood cancer survivors might benefit from cochlear implants

Childhood cancer survivors with severe to profound sensorineural hearing loss following chemotherapy or radiotherapy may be candidates for cochlear implants, US researchers believe.
Agnostic dMMR tumour PD-1 inhibitor approach may avoid resection

Patients with deficient mismatch repair (dMMR) cancers may not require surgery after 6 months of neoadjuvant treatment with the PD-1 inhibitor dostarlimab, suggests research published in The New England Journal of Medicine.
Lorundrostat shows promise for uncontrolled, treatment-resistant hypertension
Lorundrostat, a selective aldosterone synthase inhibitor, shows blood pressure -lowering potential in people with uncontrolled and treatment-resistant hypertension, according to the Advance-HTN trial.
Polygenic risk score may improve prostate cancer screening
A polygenic risk score could help direct prostate cancer screening towards those at highest risk for the disease, the BARCODE1 investigators report.